

Va
Aliasing velocity
- Manually set value on the echocardiography machine.
- It´s used to calculate: EROA.
- Nyquist limit: 50-70cm/s
- Baseline is shifted in the direction of tricuspid regurgitation jet to 30-40cm/s.
- Aliasing occurs: If the blood flow from the probe (blue) exceeds the Va speed (38.5cm/s).


VCW
Vena contracta width
- Narrowest portion of jet as emerges from tricuspid orifice.
- Vena contracta is diameter of EROA (Effective Regurgitant Orifice Area).
- A4C (RV focused)
- Zoom mode (focused on tricuspid valve).
- Color doppler
- Nyquist limit (Aliasing velocity): 50-70cm/s


PISAr
Proximal isovelocity surface area radius
- The radius of PISA is measured from the surface of the hemisphere to the narrowest portion of jet (Vena contracta).
- Vena contracta is narrowest portion of jet as emerges from tricuspid orifice.
- The flow convergence zone is the zone of increased flow velocity before the regurgitant orifice.
- It´s used to calculate: EROA.
- A4C (RV focused)
- Zoom mode (focused on tricuspid valve)
- Mid-systole (ECG: The beginning of T wave).
- Color doppler
- Nyquist limit (Aliasing velocity): 30-40cm/s


Vmax TR
Peak tricuspidal regurgitation velocity
- It´s used to calculate: EROA
- A4C (RV focused)
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave).
- CW doppler
- Place the cursor between tricuspid leaflet tips.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).



EROA
Effective regurgitant orifice area
- EROA = 2π x PISAr2 x Va / Vmax TR
- Is the narrowest area of tricuspid regurgitation flow.
- It´s used to calculate: RegVolTR


VTI TR
Velocity time integral of tricuspidal regurgitant jet
- It´s used to calculate: RegVolTR
- A4C (RV focused)
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave)
- CW doppler
- Place the cursor between tricuspid leaflet tips.
- Trace along the edge of the modal velocity to measure the area under the curve.




RegVolTR
Regurgitant volume of tricuspidal regurgitation
- RegVolTR = EROA x VTI TR
- Regurgitant volume of tricuspidal regurgitation.


RegJetsoft density
Regurgitant jet soft density
- Density and contour of regurgitant jet
- Density is proportional to the number of red blood cells reflecting the signal.
- A4C (RV focused)
- Zoom mode (focused on tricuspid valve)
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave)
- CW doppler
- Soft density suggests mild tricuspid regurgitation.


RegJethard density
Regurgitant jet hard density
- Density and contour of regurgitant jet.
- Density is proportional to the number of red blood cells reflecting the signal.
- A4C (RV focused)
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave)
- CW doppler
- Hard density suggests severe tricuspid regurgitation.
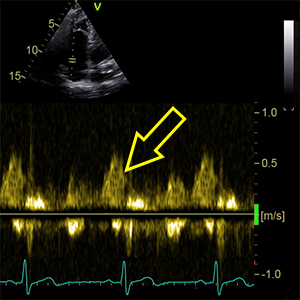

A wavedominant
Dominant tricuspidal A wave (A wave > E wave)
- A4C (RV focused).
- Late-diastole (ECG: Right after P wave)
- PW doppler.
- Sample volume between tricuspid leaflet tips.
- Suggest mild tricuspid regurgitation.


RA major
Right atrium major axis dimension
- Length of righ atrium
- A4C (RV focused).
- End-systole (ECG: The end of T wave).
- Length from center of valve annulus to center of superior RA wall
- Parallel to intraatrial septum.


RVD1basal
Right ventricular basal diameter at end-diastole
- RVD1 represents the RV’s widest diameter.
- A4C (RV focused).
- End-diastole (ECG: R wave).
- It´s measured just above the tricuspid annulus.


TVannulus
Tricuspid valve annulus diameter
- A4C (RV focused)
- Zoom mode (focused on tricuspid valve)
- End-diastole (ECG: R wave)
- The dilated tricuspid annulus suggests severe tricuspid regurgitation.
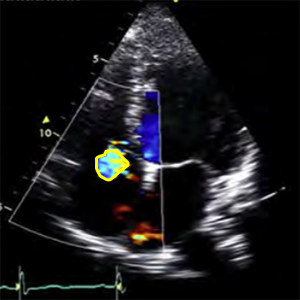

RegJetarea
Regurgitation jet area
- It´s used to calculate: RegJet/RA area
- A4C (RV focused)
- Zoom mode (focused on tricuspid valve)
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave)
- Color doppler
- Nyquist limit (Aliasing velocity): 50-70cm/s
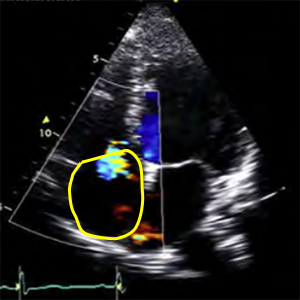

RA area
Right atrial area
- It´s used to calculate: RegJet/RA area
- A4C (RV focused)
- Zoom mode (focused on tricuspid valve)
- End-systole (ECG: The end of T wave).
- Color doppler
- Nyquist limit (Aliasing velocity): 50-70cm/s


RegJet/RA area
Ratio RegJetarea / RA area
- RegJet/RA area = RegJetarea / RA area x 100
- Ratio area of the jet to the right atrium area.

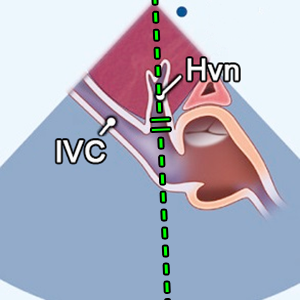
HVreversal flow
Hepatic vein reversal flow
- Hepatic vein reversal flow during systole
- SC window (Hepatic vein)
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave)
- PW doppler
- Sample volume from hepatal vein.
- Suggests severe tricuspid regurgitation


HVforward flow
Hepatic vein forward flow
- Dominant systolic flow (nonreversal, to the VCI) in hepatic vein during systole.
- SC window (Hepatic vein)
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave)
- PW doppler
- Sample volume from hepatal vein.
- Suggests mild tricuspid regurgitation


SVPV
Stroke volume of pulmonary valve
- SVPV = CSARVOT x VTIRVOT
- It´s used to calculate: TrVA
- Stroke volume of pulmonary valve is the same as stroke volume of tricuspid valve.
- If no tricuspid regurgitation is present
- Calculate it in the top menu: PV
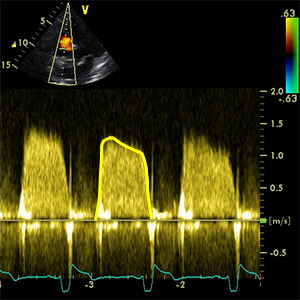

VTI TrV
Velocity time integral of tricuspid valve (inflow)
- It´s used to calculate: TrVA
- A4C (RV focused)
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- CW doppler
- Place the cursor in the middle of tricuspid valve.
- Trace along the edge of the modal velocity to measure the area under the curve.



TrVA
Tricuspid valve area (continuity equation)
- TrVA = SVPV / VTI TrV
- TrVA is underestimated if moderate or severe tricuspid regurgitation is present.
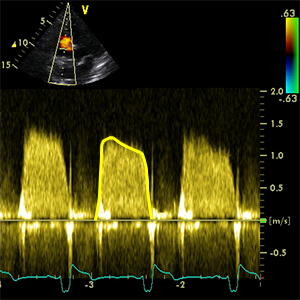

meanPG TrV
Mean pressure gradient tricuspidal valve
- A4C (RV focused)
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- CW doppler
- Place the cursor in the middle of tricuspid valve.
- Trace along the edge of the modal velocity (inflow) to measure the area under the curve.


PHT TrV
Pressure half time of tricuspidal valve
- Pressure half-time (PHT) is defined as the time interval in milliseconds between the maximum gradient and the time point where the gradient is half the maximum initial value.
- A4C (RV focused)
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- CW doppler
- Place the cursor in the middle of tricuspid valve.
- PHT is obtained by tracing the deceleration slope.


IVCdiameter
Inferior vena cava diameter
- Maxiumum inferior vena cava diameter.
- SC window (long axis IVC).
- Measured perpendicular to the long axis of the IVC at end-expiration.
- Just proximal to the junction of the hepatic veins that lie
- approximately 1-3cm proximal to the ostium of the right atrium.
References:
Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the ASE and EACVI (2015)
Recommendations for the Evaluation of LV Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the ASE and EACVI (2016)
Recommendations on the use of echocardiography in adult hypertension: a report from the EACVI and the ASE (2015)
Recommendations on the Echocardiographic Assessment of Aortic Valve Stenosis: A Focused Update from the EACVI and the ASE (2017)
ASE Recommendations for Noninvasive Evaluation of Native Valvular Regurgitation (2017)
Guidelines for performing a comprehensive TTE examination in adults: Recommendations from the ASE (2018)
Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of the Right Heart in Adults: ASE, EACVI, ESC, CSE (2010)
Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism ESC, ERS (2019)
Echocardiography in aortic diseases: EAE recommendations for clinical practice (2010)
Echocardiographic assessment of valve stenosis: EAE/ASE recommendations for clinical practice (2009)
ESSENTIAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY A Companion to Braunwald’s Heart Disease
Coronary Artery Territories (Echocardiography Illustrated Book 4)