

RVD1basal
Right ventricular basal diameter at end-diastole
- RVD1 represents the RV’s widest diameter.
- A4C (RV focused).
- End-diastole (ECG: R wave).
- It´s measured just above the tricuspid annulus.


RVD2mid
Right ventricular mid diameter at end-diastole
- RV middle size at level of papillary muscles.
- A4C (RV focused).
- End-diastole (ECG: R wave)
- It´s measured in the first third of RV at level of papillary muscles.


RVD3long
Right ventricular longitudinal diameter at end-diastole
- A4C (RV focused).
- End-diastole (ECG: R wave).
- It´s measured from the center of the tricuspid annulus to the RV apex.


RVOTprox(PLAX)
Right ventricular outflow tract dimension at proximal (PLAX)
- PLAX (Parasternal long axis).
- End-diastole (ECG: R wave).
- It´s measured in parasternal long axis (PLAX) from anterior RV wall to IVS.


RVOTprox(PSAX)
Right ventricular outflow tract dimension at proximal (PSAX)
- PSAX (level great vessels) focus on AV.
- End-diastole (ECG: R wave).
- It´s measured in parasternal short axis (PSAX) from anterior RV wall to aortic valve.


RVOTdistal(PSAX)
Right ventricular outflow tract dimension at distal
- PSAX (level great vessels) focus on PV.
- End-diastole (ECG: R wave).
- It´s measured in parasternal short axis (PSAX) proximal to pulmonic valve.
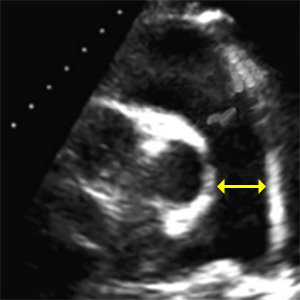

PAdiameter
Main pulmonary artery diameter
- PSAX (level great vessels) focus on PV.
- End-diastole (ECG: R wave).
- Measured between pulmonary annulus and bifurcation of the pulmonary artery.
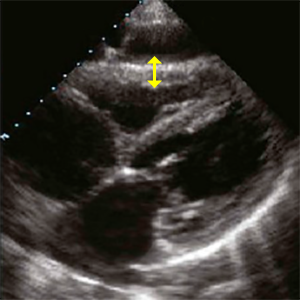
RVWT
Right ventricular wall thickness
- SC 4C (Subcostal 4 chamber) or PLAX (Parasternal long axis).
- End-diastole (ECG: R wave)
- Measured approximately in the middle of the right ventricle.


RV EDA
Right ventricular end-diastolic area
- A4C (RV focused).
- End-diastole (ECG: R wave)
- Trace only the endocardial border
- Do not trace around the trabeculations and moderator bands
- these should remain inside the RV cavity. - Include the apex and entire free wall


RV ESA
Right ventricular end-systolic area
- A4C (RV focused).
- End-systole (ECG: The end of T wave)
- Trace only the endocardial border
- Do not trace around the trabeculations and moderator bands
- these should remain inside the RV cavity. - Include the apex and entire free wall


FAC
Fractional Area Change
- FAC = (RV EDA - RV ESA) / RV EDA x 100
- Based upon area change (RV EDA vs RV ESA)
– the value will be less than the calculated RV ejection fraction value. - FAC is the percentage of area change not the RV ejection fraction.


RV EDV
Right ventricular end-diastolic volume
- A4C (RV focused).
- The right ventricle does not have the ellipsoid shape like the left ventricle.
- Therefore, 2D methods are not recommended when measuring right ventricular volumes: (area-length, method of discs).
- A 3D method is recommended for measuring right ventricular volumes.
- The 3D method must be supported by the echocardiography machine.


RV ESV
Right ventricular end-systolic volume
- A4C (RV focused).
- The right ventricle does not have the ellipsoid shape like the left ventricle.
- Therefore, 2D methods are not recommended when measuring right ventricular volumes: (area-length, method of discs).
- A 3D method is recommended for measuring right ventricular volumes.
- The 3D method must be supported by the echocardiography machine.


RV EF
Right ventricular ejection fraction
- RV EF = (RV EDV - RV ESV) / RV EDV x 100
- Ejection fration of right ventricla is calculated from RV EDV and RV ESV by
- specific 3D echocardiographic software.

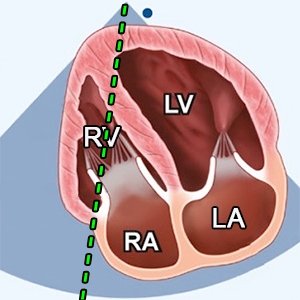
TAPSE
Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion
- TAPSE measures the longitudinal excursion of the tricuspid annulus by M-mode.
- A4C (RV focused).
- Systole-diastole (ECG: R wave - R wave)
- M-mode.
- Align M-Mode cursor parallel to motion of lateral TV annulus
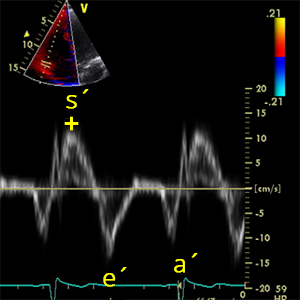

S´wavepulsedTDI
Peak systolic velocity of the tricuspid annulus (Pulsed TDI)
- A4C (RV focused).
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave).
- PW tissue Doppler imaging (TDI)
- Place cursor over lateral annulus of tricuspid valve
- Identify maximum systolic velocity ABOVE the baseline: S´ wave
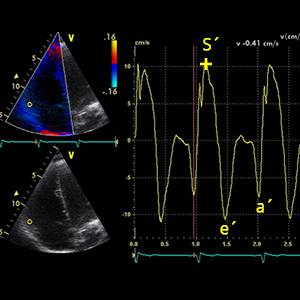

S´wavecolorTDI
Peak systolic velocity of the tricuspid annulus (Color TDI)
- A4C (RV focused).
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave).
- Color Tissue Doppler Imaging (TDI)
- Place cursor over lateral annulus of tricuspid valve
- Identify maximum systolic velocity ABOVE the baseline: S´ wave


ETRVOT(TDI)
Ejection time of RVOT (Pulsed TDI)
- It´s used to calculate: RIMPTDI
- A4C (RV focused)
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave).
- PW tissue Doppler imaging (TDI).
- Place cursor over lateral annulus of tricuspid valve
- ETRVOT(TDI) represented by the duration of the S’ Wave.


TCOTrV(TDI)
Tricuspid valve closure to open time (Pulsed TDI)
- It´s used to calculate: RIMPTDI
- A4C (RV focused)
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave).
- PW tissue Doppler imaging (TDI).
- Place cursor over lateral annulus of tricuspid valve
- Measured from end of a´ waveTrV to beginning of the following e´ waveTrV.


RIMPTDI
Right Ventricular Index of Myocardial Performance (TDI)
- RIMPTDI = (TCOTrV(TDI) – ETRVOT(TDI)) / ETRVOT(TDI)
- RIMP represents the relationship between the ejection and non-ejection time of the heart.
- Also know as:
- MPI (Myocardial performance index)
- Tei index
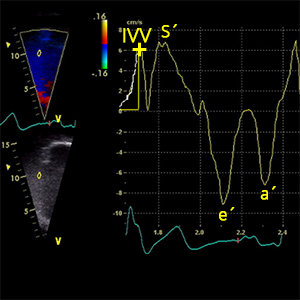

IVVRV
Peak myocardial velocity during isovolumic contraction
- It´s used to calculate: IVARV
- A4C (RV focused).
- Early-systole (ECG: Right after R wave).
- Color Tissue Doppler Imaging (TDI)
- Place cursor over lateral annulus of tricuspid valve.


ATRV
Acceleration time during isovolumic contraction
- It´s used to calculate: IVARV
- A4C (RV focused).
- Early-systole (ECG: Right after R wave).
- Color Tissue Doppler Imaging (TDI)
- Place cursor over lateral annulus of tricuspid valve.


IVARV
Myocardial acceleration during isovolumic contraction
- IVARV = IVVRV / ATRV
- IVARV >1,1m/s2 correlates with RV EF >45%.

PVR
Pulmonary vascular ressistance
- PVR = (Vmax TR / VTIRVOT) x 10 + 0,16
- An elevation in SPAP does not always imply an increased PVR.
- PVR distinguishes elevated pulmonary pressure due to high flow from that due to pulmonary vascular disease.
- PVR plays an important role in patients with heart failure with regard to transplantation eligibility.


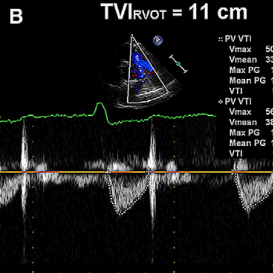
VTIRVOT
Velocity time integral of right ventricular outflow tract
- It´s used to calculate: PVR
- PSAX (level great vessels) focus on PV.
- Zoom mode (focused on RVOT).
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave).
- PW doppler
- Place sample volume in the middle of RVOT.


Vmax TR
Peak tricuspidal regurgitation velocity
- It´s used to calculate: PVR
- A4C (RV focused).
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave).
- CW doppler.
- Place the cursor between tricuspid leaflet tips.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).


1 to 2m/s TRtime
Time interval between 1 and 2 m/sec on tricuspid regurgitation velocity
- It´s used to calculate: RV dP/dt
- A4C (RV focused).
- Early-systole (ECG: Right after R wave)
- CW doppler.
- Place the cursor between tricuspid leaflet tips.
- Point 3 is measured:
- Point 1 represents the point at which the TR signal meets the 1 m/s.
- Point 2 represents the point at which the TR signal meets the 2 m/s
- Point 3 represents the time required for the TR jet to increase from 1 to 2 m/s.


RV dP/dt
Rate of rise of right ventricle pressure
- RV dP/dt = 12 / (1 to 2m/s TRtime)
- A4C (RV focused).
- In this example:
- 1 to 2m/s TRtime = 0,03s
- The RV dP/dt is therefore 12mmHg/0.03s = 400mmHg/s.
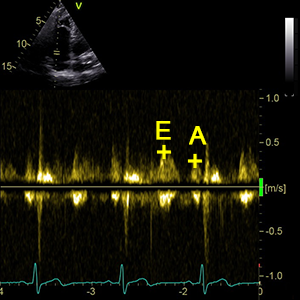

E/ATrV
Tricuspid valve E / A ratio
- E/ATrV = E-waveTrV / A-waveTrV
- E/ATrV is the ratio of the early (E-waveTrV) to late (A-waveTrV) right ventricular filling velocities.


E-waveTrV
Peak velocity in early diastole (Tricuspid valve)
- It´s used to calculate: E/ATrV a E/e´TrV
- A4C (RV focused)
- Early-diastole (ECG: The end of T wave).
- PW doppler
- Sample volume (1–3 mm axial size) between tricuspid leaflet tips.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).
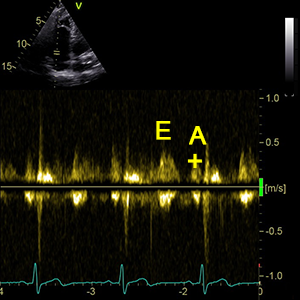

A-waveTrV
Peak velocity in late diastole (Tricuspid valve)
- It´s used to calculate: E/ATrV
- A4C (RV focused)
- Late-diastole (ECG: Right after P wave)
- PW doppler
- Sample volume (1–3 mm axial size) between tricuspid leaflet tips.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).


DT TrV
Tricuspid valve deceleration time
- Time from peak to zero-baseline of the tricuspidal E-wave velocity.
- A4C (RV focused)
- Early-diastole (ECG: The end of T wave)
- PW doppler
- Sample volume (1–3 mm axial size) between tricuspid leaflet tips.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).


e´ waveTrV
Peak velocity in early diastole of the tricuspid annulus (TDI)
- It´s used to calculate: E/e´TrV a e´/a´TrV
- A4C (RV focused)
- Early-diastole (ECG: The end of T wave)
- PW tissue Doppler imaging (TDI)
- Sample volume on lateral tricuspid annulus.


E/e´TrV
Tricuspid valve E / e´ ratio
- E/e´TrV = E-waveTrV / e´ waveTrV
- E/e´TrV is ratio of the E-waveTrV and e´ waveTrV
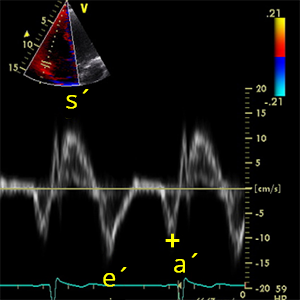

a´ waveTrV
Peak velocity in late diastole of the tricuspid annulus (TDI)
- It´s used to calculate: e´/a´TrV
- A4C (RV focused)
- Late-diastole (ECG: Right after P wave)
- PW tissue Doppler imaging (TDI)
- Sample volume on lateral tricuspid annulus.


e´/a´TrV
Tricuspid valve e´ / a´ ratio (TDI)
- e´/a´TrV = e´ waveTrV / a´ waveTrV
- e´/a´TrV is ratio of the e´ waveTrV and a´ waveTrV
- A4C (RV focused).
References:
Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the ASE and EACVI (2015)
Recommendations for the Evaluation of LV Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the ASE and EACVI (2016)
Recommendations on the use of echocardiography in adult hypertension: a report from the EACVI and the ASE (2015)
Recommendations on the Echocardiographic Assessment of Aortic Valve Stenosis: A Focused Update from the EACVI and the ASE (2017)
ASE Recommendations for Noninvasive Evaluation of Native Valvular Regurgitation (2017)
Guidelines for performing a comprehensive TTE examination in adults: Recommendations from the ASE (2018)
Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of the Right Heart in Adults: ASE, EACVI, ESC, CSE (2010)
Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism ESC, ERS (2019)
Echocardiography in aortic diseases: EAE recommendations for clinical practice (2010)
Echocardiographic assessment of valve stenosis: EAE/ASE recommendations for clinical practice (2009)
ESSENTIAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY A Companion to Braunwald’s Heart Disease
Coronary Artery Territories (Echocardiography Illustrated Book 4)