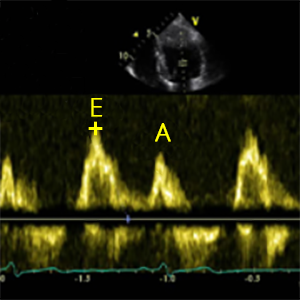
E-wave
Peak velocity in early diastole (Passive flow)
- It´s used to calculate: MV E/A, MV E/e´, Lateral E/e´, E/VpcolorM
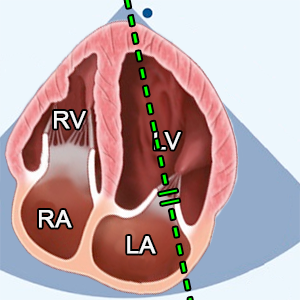
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber).
- Early-diastole (ECG: The end of T wave).
- PW doppler.
- Sample volume (1–3 mm axial size) between mitral leaflet tips.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).


A-wave
Peak velocity in late diastole (Atrial contraction)
- It´s used to calculate: MV E/A
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber).
- Late-diastole (ECG: Right after P wave)
- PW doppler.
- Sample volume (1–3 mm axial size) between mitral leaflet tips.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).


MV E/A
Mitral valve E-wave/A-wave ratio
- MV E/A = E-wave / A-wave
- MV E/A is the ratio of the early (E-wave) to late (A-wave) ventricular filling velocities.
- It is a first generation test for diastolic performance of the heart.
Valsalva maneuver
Valsalva maneuver
- Recording obtained continuously through peak inspiration and as patient performs forced expiration for 10 sec with mouth and nose closed.
- Change in mitral inflow with Valsalva: ≥50% change in MV E/A
- is highly specific for increased LV filling pressures,
- and supports diagnosis of diastolic dysfunction
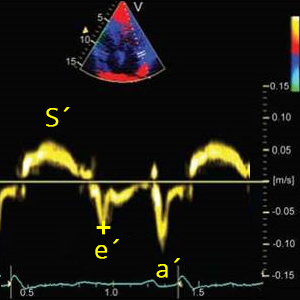
Lateral e´
Lateral mitral annulus velocity (Early diastole)
- It´s used to calculate: Average e´, Lateral E/e´
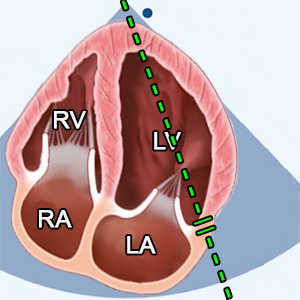
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber).
- Early-diastole (ECG: The end of T wave).
- PW tissue Doppler imaging (TDI)
- Sample volume on lateral mitral basal regions.


Septal e´
Septal mitral annulus velocity (Early diastole)
- It´s used to calculate: Average e´
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber).
- Early-diastole (ECG: The end of T wave).
- PW tissue Doppler imaging (TDI)
- Sample volume on septal basal regions.


Average e´
Average e´
- Average e´= (Lateral e´+ Septal e´) / 2
- Average value of lateral and septal e´.
- It´s used to calculate: MV E/e´


MV E/e´
Mitral valve E-wave / Average e´ ratio
- MV E/e´= E-wave / Average e´
- The ratio between E-wave and Average e´.


Vmax TR
Peak tricuspid regurgitation systolic jet velocity
- A4C (RV focused).
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave).
- CW doppler
- Place the cursor between tricuspid leaflet tips.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).


LA volume
Left atrial volume (Biplane)
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber) and A2C (Apical 2 chamber).
- End-systole (ECG: The end of T wave)
- Volume can be calculated by the area-length method or disk summation technique (modified biplane) which is preferred.
- Trace the LA inner border, excluding the area under the MV annulus, pulmonary veins, and LA appendage.
- Volume is calculated from A4C and A2C by echocardiography machine.
- Calculate it in the top menu: Atria and IVC.


Lateral E/e´
MV E-wave / Lateral e´ ratio
- Lateral E/e´= E-wave / Lateral e´
- The ratio between E-wave and lateral e´.
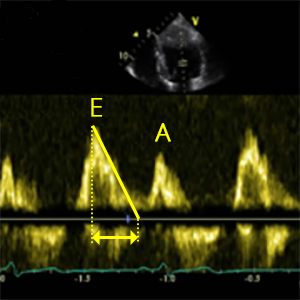

MV DT
Mitral valve deceleration time
- Peak E-wave along slope of LV filing extrapolated to zero-velocity baseline
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber).
- Early-diastole (ECG: The end of T wave)
- PW doppler.
- Sample volume (1–3 mm axial size) between mitral leaflet tips.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).

PV S wave
Pulmonary vein peak velocity (Early systole)
- It´s used to calculate: PV S/D ratio
- A4C (LA pulmonary veins focus).
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave)
- PW doppler
- Sample volume from right (or left) pulmonary vein.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).

PV D wave
Pulmonary vein peak velocity (Early diastole)
- It´s used to calculate: PV S/D ratio
- A4C (LA pulmonary veins focus).
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- PW doppler
- Sample volume from right (or left) pulmonary vein.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).


PV S/D ratio
Pulmonary vein S/D wave ratio
- PV S/D ratio = PV S wave / PV D wave
- The ratio between PV S wave and PV D wave.


PV S VTI
Pulmonary vein S wave velocity time integral
- It´s used to calculate: PVsys.fraction
- A4C (LA pulmonary veins focus).
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave)
- PW doppler
- Sample volume from right (or left) pulmonary vein.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).


Total PV VTI
Total pulmonary vein inflow velocity time integral
- It´s used to calculate: PVsys.fraction
- A4C (LA pulmonary veins focus).
- Systole and diastole (ECG: R wave - R wave)
- PW doppler
- Sample volume from right (or left) pulmonary vein.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).


PVsys.fraction
Pulmonary vein systolic filling fraction
- PVsys.fraction = PV S VTI / Total PV VTI x 100
- The systolic fraction of the pulmonary vein flow velocity-time integral, a ratio of velocity-time integral of the S wave (PV S VTI) to the sum of velocity-time integrals of the S and D waves (Total PV VTI),
- represents the ratio of left atrial storage volume to left ventricular stroke volume.


PV ARduration
Pulmonary vein atrial reversal flow duration
- It´s used to calculate: AR-A
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber).
- Atrial systole (ECG: Right after P wave)
- PW doppler
- Sample volume from right (or left) pulmonary vein.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).


MV Aduration
Mitral valve A-wave duration
- It´s used to calculate: AR-A
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber).
- Late-diastole (ECG: Right after P wave).
- PW doppler.
- Sample volume (1–3 mm axial size) between mitral leaflet tips.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).


AR-A
Time difference (PV ARduration - MV A duration)
- AR-A = PV ARduration - MV Aduration
- The comparison of time duration between the pulmonary venous antegrade (PV ARduration) and transmitral A-wave velocity can be used to estimate the LVEDP.
- An AR-A duration >30 ms is consistent with elevated LVEDP (left ventricular end-diastolic pressure).


L wave
Transmitral flow during diastasis
- This wave indicates continued pulmonary vein flow through the left atrium (LA) into the left ventricle (LV) after early rapid filling.
- Several investigations have shown that its presence is correlated with symptoms, prognosis, and elevated filling pressures.
- Mid-diastole (ECG: The beginning of P wave)
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber).
- PW doppler.
- Sample volume (1–3 mm axial size) between mitral leaflet tips.

VpcolorM
Transmitral flow propagation velocity (Color Doppler M-mode)
- This method is basically a means of determining how rapidly blood travels from the base of the ventricle towards the apex.
- To measure flow propagation one measures the slope of the aliased signal (blue) from the mitral valve plane 4 cm into the ventricle.
- It´s used to calculate: E/VpcolorM
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber).
- Early-diastole (ECG: The end of T wave).
- Color doppler
- Nyquist limit (Aliasing): 30cm/s
- M-mode
- Place the M-mode line between mitral leaflet tips.


E/VpcolorM
E wave and transmitral flow propagation velocity ratio
- E/VpcolorM = E-wave / VpcolorM
- E/VpcolorM correlates with LAP (Left atrial pressure).
- E/VpcolorM ≥2,5 predicts PCWP > 15mmHg g with reasonable accuracy in patients with depressed LV EF.
- PCWP (Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure)


AccRE wave
Peak acceleration rate of mitral inflow E wave
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber).
- Early-diastole (ECG: The end of T wave)
- PW doppler.
- Sample volume (1–3 mm axial size) between mitral leaflet tips.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).
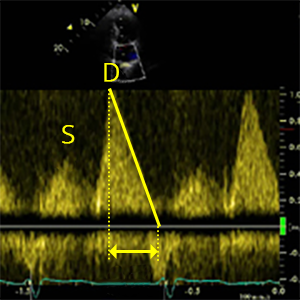

PV DTD wave
Deceleration time of pulmonary venous diastolic velocity
- Peak PV D wave along slope of LA filing extrapolated to zero-velocity baseline
- A4C (LA pulmonary veins focus).
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- PW doppler
- Sample volume from right (or left) pulmonary vein.
- Color doppler (helps with blood flow identification).
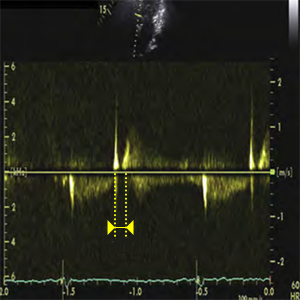
IVRT
Isovolumic Relaxation Time
- Time between aortic valve closure and MV opening.
- It´s used to calculate: IVRT/TT-e´
- A5C (Apical 5 chamber),
A3C or APLAX (Apical 3 chamber, Apical long axis) - Early-diastole (ECG: The end of T wave).
- CW doppler
- Using CW Doppler and placing sample volume in LV outflow tract to simultaneously display end of aortic ejection and onset of mitral inflow.


QRS-Septal e´
Time difference from onset of QRS and septal e´
- Time from the R wave (on ECG) to the beginning of the septal e´ wave
- It´s used to calculate: T E-e´
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber).
- Systole - Early diastole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave)
- PW tissue Doppler imaging (TDI)
- Sample volume on septal basal regions.


QRS-E wave
Time difference from onset of QRS and E wave
- Time from the R wave (on ECG) to the beginning of the E-wave
- It´s used to calculate: T E-e´
- A4C (Apical 4 chamber).
- Systole - Early diastole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave)
- PW doppler
- Sample volume (1–3 mm axial size) between mitral leaflet tips.


TE-e´
Time difference from onset of E wave and e´
- TE-e´ = QRS-Septal e´ - QRS-E wave
- Can identify patients with diastolic dysfunction due to delayed onset of e´ velocity compared with onset of mitral E velocity


IVRT/TE-e´
Isovolumic Relaxation Time and Time difference from onset of E wave and e´ ratio
- IVRT/TE-e´ = IVRT / TE-e´
- Ratio of IVRT to TE-e´ can be used to estimate LV filling pressures in normal subjects and patients with mitral valve disease.
References:
Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the ASE and EACVI (2015)
Recommendations for the Evaluation of LV Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the ASE and EACVI (2016)
Recommendations on the use of echocardiography in adult hypertension: a report from the EACVI and the ASE (2015)
Recommendations on the Echocardiographic Assessment of Aortic Valve Stenosis: A Focused Update from the EACVI and the ASE (2017)
ASE Recommendations for Noninvasive Evaluation of Native Valvular Regurgitation (2017)
Guidelines for performing a comprehensive TTE examination in adults: Recommendations from the ASE (2018)
Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of the Right Heart in Adults: ASE, EACVI, ESC, CSE (2010)
Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism ESC, ERS (2019)
Echocardiography in aortic diseases: EAE recommendations for clinical practice (2010)
Echocardiographic assessment of valve stenosis: EAE/ASE recommendations for clinical practice (2009)
ESSENTIAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY A Companion to Braunwald’s Heart Disease
Coronary Artery Territories (Echocardiography Illustrated Book 4)