

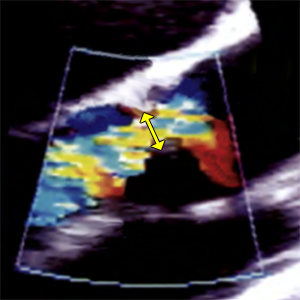
Va
Aliasing velocity
- Manually set value on the echocardiography machine.
- It´s used to calculate: EROA.
- Nyquist limit: 50-70cm/s
- Baseline is shifted in the direction of aortic regurgitation jet to 30-40cm/s.
- Aliasing occurs: If the blood flow to the probe (red) exceeds the Va speed (38.5cm/s)

VCW
Vena contracta width
- Narrowest portion of jet as emerges from aortic orifice.
- Vena contracta is diameter of EROA (Effective Regurgitant Orifice Area).
- PLAX (zoomed AV)
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- Color doppler
- Nyquist limit (Aliasing velocity): 50-70cm/s


PISAr
Proximal isovelocity surface area radius
- The radius of PISA is measured from the surface of the hemisphere to the narrowest portion of jet (Vena contracta).
- Vena contracta is narrowest portion of jet as emerges from aortic orifice.
- The flow convergence zone is the zone of increased flow velocity before the regurgitant orifice
- It´s used to calculate: EROA
- A5C (Apical 5 chamber) or PLAX (Parasternal long axis)
- Zoom mode (focused on aortic valve)
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- Color doppler
- Nyquist limit (Aliasing velocity): 30-40cm/s


Vmax AR
Peak aortic regurgitation velocity
- It´s used to calculate: EROA.
- A5C (Apical 5 chamber)
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- CW doppler
- Place the cursor between aortic leaflet tips.



EROA
Effective regurgitant orifice area
- EROA = 2π x PISAr2 x Va / Vmax AR
- Is the narrowest area of aortic regurgitation flow.


RegJetwidth
Regurgitation jet width
- It´s used to calculate: RegJetwidth in LVOT
- PLAX (zoomed AV)
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- Color doppler
- Nyquist limit (Aliasing velocity): 50-70cm/s
- Measured in LVOT 1cm from vena contracta.


LVOTdiameter
Left ventricular outflow tract diameter
- It´s used to calculate: CSALVOT, SVAoV a RegJetwidth in LVOT, AVA
- PLAX (zoomed AV)
- Mid-systole (ECG: The beginning of T wave)
- Measured in LVOT 5mm from aortic annulus.
- Excluded calcium from the diameter measurement.
- Method: Inner edge to inner edge


RegJetwidth in LVOT
Regurgitation jet width in left ventricular outflow tract
- RegJetwidth in LVOT = RegJetwidth/LVOTdiameter x 100
- Is the percentage regurgitant jet width in the LVOT
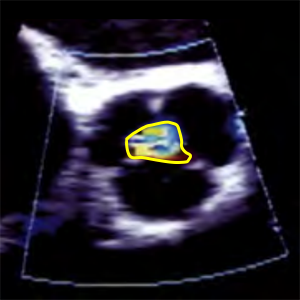
CSARegJet
Regurgitation jet cross section area
- It´s used to calculate: CSARegJet in CSA LVOT.
- PSAX (level great vessels) zoomed AV
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- Color doppler
- Nyquist limit (Aliasing velocity): 50-70cm/s
- Measured in LVOT 1cm from vena contracta.


CSARegJet in CSA LVOT
Regurgitation jet cross section area (CSA) in LVOT CSA
- Is the percentage area of the jet to the LVOT area.


RegJetsoft density
Regurgitant jet soft density
- Density and contour of regurgitant jet
- Density is proportional to the number of red blood cells reflecting the signal
- A5C (Apical 5 chamber)
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- CW doppler
- Compare density with nonregurgitant flow
- Dense signal suggests significant AR, whereas a faint signal is likely to be mild or trace AR.


PHTRegJet
Pressure half time of regurgitant jet
- Pressure half-time (PHT) is defined as the time interval in milliseconds between the maximum gradient and the time point where the gradient is half the maximum initial value.
- A5C (Apical 5 chamber)
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- CW doppler
- PHT is obtained by tracing the deceleration slope.


RevFlowDesAo
Reversal holodiastolic flow in descending aorta
- SSN window (aortic arch)
- Diastole (ECG: The end of T wave - R wave)
- PW doppler
- Sample volume from proximal part of the descending aorta.
- Suggest severe aortic regurgitation


SVMV
Stroke volume of mitral valve
- SVMV = CSAMV x VTI MV
- It´s used to calculate: RegVolAR
- Calculate it in the top menu: MV


VTILVOT
Velocity time integral of left ventricular outflow tract
- It´s used to calculate: SVAoV, AVA
- A5C (Apical 5 chamber)
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave).
- PW doppler
- Sample volume from the center of the LVOT approximately 5 mm proximal to the aortic annulus.
- Exactly to the level where the LVOTdiameter was measured.
- Trace along the edge of the modal velocity to measure the area under the curve.


SVAoV
Stroke volume via left ventricular outflow tract (aortic valve)
- SVAoV = CSALVOT x VTILVOT
- It´s used to calculate: RegVolAR, RFAR




RegVolAR
Regurgitant volume of aortic regurgitation
- RegVolAR = SVAoV - SVMV
- It´s used to calculate: RFAR




RFAR
Regurgitant fraction
- RFAR = RegVolAR / SVAoV x 100
- Regurgitation fraction of aortic regurgitation.


LV EF
Left ventricular ejection fraction (Biplane Method of Discs)
- LV EF = (LVEDV - LVESV) / LVEDV x 100
- Ejection fraction is the predominant method for assessing global systolic function
- and is derived from the LVEDV and LVESV.
- Calculate it in the top menu: Left ventricle


LVEDV
Left ventricular end-diastole volume
- A4C (zoomed left ventricle) and A2C (zoomed left ventricle).
- End-diastole (ECG: R wave).
- Preferred technique is Biplane Method of Discs (modified Simpson’s rule).
- Measured from the A4C and A2C views (preferably an LV focused view) tracing the endocardial – blood pool interface
- Papillary muscles should be excluded from the cavity tracing.
- Maximize LV area and avoid foreshortening.
- Calculate it in the top menu: Left ventricle


VTI AoV
Velocity time integral aortic valve
- It´s used to calculate: AVA
- A5C (Apical 5 chamber).
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave).
- CW doppler
- Place the cursor in the middle of aortic valve.
- Trace along the edge of the modal velocity to measure the area under the curve.




AVA
Aortic valve area (continuity equation)
- AVA = CSALVOT x VTILVOT / VTI AoV
- Aortic valve area calculation with the continuity equation formula is an indirect method of determining the area of the aortic valve (aortic valve area).
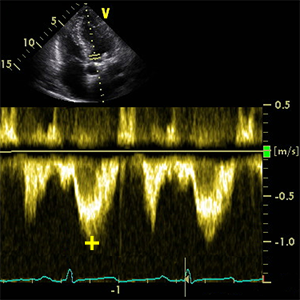

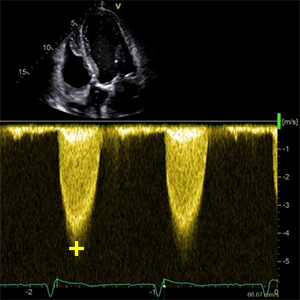
VmaxLVOT
Peak velocity Left ventricular aoutflow tract
- It´s used to calculate: Velocity ratio
- A5C (Apical 5 chamber)
- Mid-systole (ECG: The beginning of T wave).
- PW doppler
- Sample volume from the center of the LVOT approximately 5 mm proximal to the aortic annulus.
- Exactly to the level where the LVOTdiameter was measured.

Vmax AoV
Aortic valve maximum velocity
- It´s used to calculate: Velocity ratio
- A5C (Apical 5 chamber).
- Mid-systole (ECG: The beginning of T wave)
- CW doppler
- Place the cursor in the middle of aortic valve.


Velocity ratio
Aortic valve velocity ratio (Dimensionless index)
- Velocity ratio = VmaxLVOT / Vmax AoV
- Ratio of the subvalvular velocity obtained by PW doppler (VmaxLVOT) and the maximum velocity obtained by CW doppler (Vmax AoV) across the aortic valve.
- Also know as: Dimensionless index


maxPG AoV
Aortic valve peak pressure gradient
- A5C (Apical 5 chamber).
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave).
- CW doppler
- Place the cursor in the middle of aortic valve.


meanPG AoV
Aortic valve mean pressure gradient
- A5C (Apical 5 chamber).
- Systole (ECG: R wave - The end of T wave).
- CW doppler
- Place the cursor in the middle of aortic valve.
- Trace along the edge of the modal velocity to measure the area under the curve.
References:
Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the ASE and EACVI (2015)
Recommendations for the Evaluation of LV Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the ASE and EACVI (2016)
Recommendations on the use of echocardiography in adult hypertension: a report from the EACVI and the ASE (2015)
Recommendations on the Echocardiographic Assessment of Aortic Valve Stenosis: A Focused Update from the EACVI and the ASE (2017)
ASE Recommendations for Noninvasive Evaluation of Native Valvular Regurgitation (2017)
Guidelines for performing a comprehensive TTE examination in adults: Recommendations from the ASE (2018)
Guidelines for the Echocardiographic Assessment of the Right Heart in Adults: ASE, EACVI, ESC, CSE (2010)
Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism ESC, ERS (2019)
Echocardiography in aortic diseases: EAE recommendations for clinical practice (2010)
Echocardiographic assessment of valve stenosis: EAE/ASE recommendations for clinical practice (2009)
ESSENTIAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY A Companion to Braunwald’s Heart Disease
Coronary Artery Territories (Echocardiography Illustrated Book 4)

